Blockchain enhances cyber security by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger. It ensures data integrity and prevents unauthorized access.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing cyber security. Its decentralized nature eliminates single points of failure, making it harder for hackers to breach systems. The immutable ledger records every transaction, ensuring transparency and traceability. Cryptographic techniques used in blockchain protect data from tampering and unauthorized access.
These features make blockchain a robust solution for securing sensitive information. Companies across various industries are increasingly adopting blockchain to safeguard their digital assets. The technology offers a promising future for enhancing cyber security measures. Integrating blockchain with existing security frameworks can significantly reduce cyber threats and data breaches, ensuring a safer digital environment.
Introduction To Blockchain
Blockchain technology has revolutionized many industries, including cyber security. This innovation offers a new way to ensure data integrity and security. Let’s dive into the basics of blockchain.
Origins And Evolution
Blockchain started with the creation of Bitcoin in 2009. Satoshi Nakamoto invented it. The primary goal was to enable secure digital transactions.
Over the years, blockchain has evolved. It now serves various sectors beyond finance. These include supply chain management, healthcare, and cyber security.
The technology has seen numerous improvements. New algorithms and protocols enhance its efficiency and security.
Core Concepts
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger. It records transactions across many computers. This makes the data hard to alter.
Each record in the blockchain is called a “block.” These blocks link together to form a chain. Every block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This ensures data integrity.
Blockchain uses consensus mechanisms. These ensure all participants agree on the data. Common methods include Proof of Work and Proof of Stake.
Smart contracts are another key concept. These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They automate and enforce agreements without intermediaries.
In cyber security, blockchain offers several advantages. It provides transparency, immutability, and decentralized control. This makes it harder for hackers to compromise data.
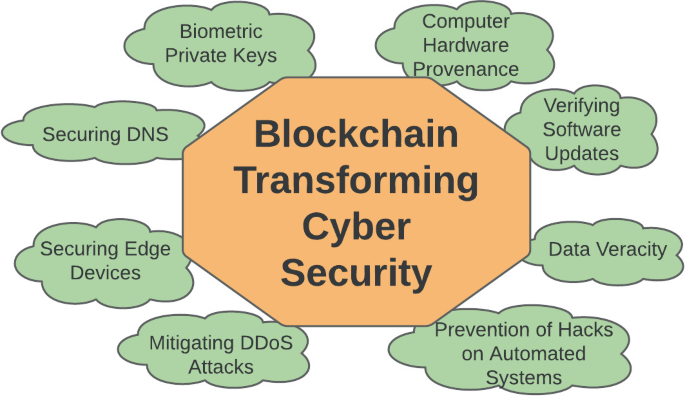
Credit: link.springer.com
Cyber Security Challenges
Cyber security faces many challenges today. Hackers are always finding new ways to attack. Traditional methods often fail to protect us. Blockchain technology could help solve these problems.
Current Threat Landscape
The current threat landscape is full of dangers. Hackers use malware, phishing, and ransomware. They steal sensitive data and cause financial losses. Businesses and individuals suffer daily.
Some common cyber threats include:
- Malware: Software designed to harm or exploit devices.
- Phishing: Fake emails that trick users into giving personal information.
- Ransomware: Malware that locks data and demands payment to unlock it.
These threats evolve quickly. Keeping up with them is hard. Traditional security methods often fall short.
Limitations Of Traditional Methods
Traditional cyber security methods have limitations. Firewalls and antivirus software can’t stop all attacks. They rely on known threats. New threats bypass these defenses easily.
| Traditional Method | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Firewalls | Can’t detect new, unknown threats. |
| Antivirus Software | Relies on databases of known viruses. |
| Intrusion Detection Systems | Often generate false positives. |
These methods also face issues like:
- High false-positive rates.
- Inability to detect zero-day attacks.
- Resource-intensive maintenance.
Blockchain offers new ways to tackle these challenges. It can enhance cyber security with its unique features.
Blockchain Fundamentals
Understanding blockchain is key to grasping its role in cyber security. Blockchain technology offers unique features that enhance security and trust. This section covers two core principles: decentralization and immutability.
Decentralization
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network. No single entity controls the entire system. This structure makes it more secure against attacks. Traditional systems rely on central servers. These central servers are vulnerable to hacking.
In a decentralized network, data is distributed. Every participant has a copy of the entire blockchain. If one node is compromised, the rest remain secure. This ensures data integrity across the network.
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Data Storage | Single Location | Distributed |
| Security | Vulnerable | Robust |
Immutability
Once recorded, blockchain data cannot be altered. This characteristic is called immutability. It ensures data remains unchanged and tamper-proof. This is vital for cyber security.
In traditional databases, data can be modified. This poses a risk of unauthorized changes. With blockchain, any attempt to alter data is immediately noticeable. This transparency is a powerful security feature.
- Immutable records strengthen trust.
- Prevents data corruption.
- Enhances auditability.
Immutability ensures that blockchain remains a reliable source of truth. It supports secure transactions and data integrity.
Blockchain In Cyber Security
Blockchain technology has revolutionized many industries. One of its significant impacts is in cyber security. By ensuring data integrity and enhancing privacy, blockchain offers robust solutions. It can protect against data breaches and cyber threats. This innovative technology is becoming crucial in safeguarding digital information.
Data Integrity
Data integrity is vital for trust in digital systems. Blockchain ensures data remains untampered. Each transaction is recorded in a block. This block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain. This structure makes it nearly impossible to alter any data. Blockchain verifies each transaction through consensus mechanisms. It ensures data accuracy and reliability.
The table below illustrates the process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Transaction initiated |
| 2 | Transaction verified by nodes |
| 3 | Transaction recorded in a block |
| 4 | Block added to the chain |
Enhanced Privacy
Privacy is a major concern in the digital age. Blockchain enhances privacy through encryption. Each user’s identity is protected by cryptographic keys. This means only authorized parties can access the data. Blockchain also offers decentralized storage. Data is not stored in a single location. This decentralization makes it harder for hackers to access sensitive information.
Key benefits of enhanced privacy include:
- Reduced risk of data breaches
- Greater control over personal information
- Increased trust in digital transactions
In the future, blockchain’s role in cyber security will grow. Its ability to ensure data integrity and enhance privacy is unmatched. Embracing this technology can lead to a safer digital world.
Real-world Applications
Blockchain technology offers a robust solution for cyber security. Its decentralized nature provides high security and transparency. Below are some real-world applications where blockchain is making an impact.
Identity Management
Managing identities securely is crucial in the digital age. Blockchain can ensure safe and efficient identity management.
- Decentralized Identification: Blockchain allows for decentralized IDs. This reduces the risk of identity theft.
- Immutable Records: All transactions are immutable. They cannot be altered or deleted.
- Data Encryption: Blockchain uses advanced encryption. This ensures that personal data remains private.
These features make blockchain a strong contender for identity management. Governments and companies are exploring its potential.
Secure Data Sharing
Data sharing is vital but risky. Blockchain provides a secure way to share data.
- Secure Access: Only authorized users can access the data.
- Traceability: Blockchain tracks all data transactions. This ensures full traceability.
- Data Integrity: Data cannot be tampered with. This ensures data integrity.
These features make blockchain ideal for secure data sharing. It is used in healthcare, finance, and other sectors.
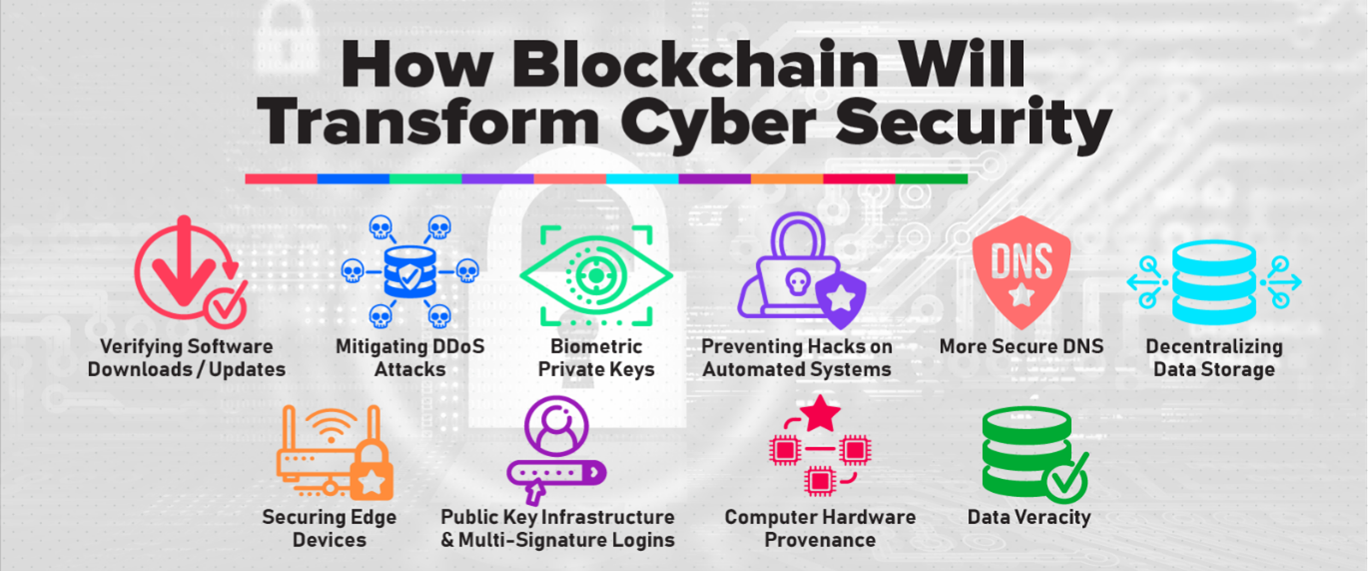
Credit: www.encora.com
Case Studies
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing cyber security across various industries. This section explores compelling case studies in different sectors. These examples illustrate how blockchain enhances security and trust.
Financial Sector
The financial sector often faces cyber threats. Blockchain technology provides a secure solution. Here are two key case studies:
| Bank | Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| JPMorgan Chase | Quorum Blockchain | Enhanced transaction security |
| Bank of America | Private Blockchain Network | Reduced fraud cases |
JPMorgan Chase uses the Quorum blockchain. This blockchain ensures secure and transparent transactions. Bank of America implemented a private blockchain network. This network helps reduce fraud cases.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector handles sensitive data. Blockchain enhances data security and integrity. Here are two notable case studies:
- MedRec: This blockchain system secures patient records. It ensures only authorized access.
- Guardtime: This company uses blockchain to secure healthcare records. The system detects tampering instantly.
MedRec secures patient records with blockchain technology. Only authorized personnel can access these records. Guardtime uses blockchain to protect healthcare data. Their system detects tampering in real time.
Future Prospects
The future of blockchain in cyber security holds exciting potential. As technology evolves, blockchain offers promising solutions to many cyber threats. Let’s explore the prospects of blockchain in enhancing cyber security.
Emerging Trends
Blockchain technology is constantly evolving. New trends are emerging that could revolutionize cyber security. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Decentralized Identity Management: Blockchain enables secure, decentralized identity systems. This reduces the risk of identity theft.
- Blockchain-based Authentication: Blockchain can provide robust, tamper-proof authentication methods.
- Smart Contracts: Automate and secure transactions using self-executing contracts.
- Supply Chain Security: Ensure product authenticity and traceability with blockchain.
Potential Challenges
Despite its promise, blockchain faces challenges in cyber security. Understanding these challenges is crucial for widespread adoption.
| Challenge | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Blockchain networks can become slow with high data volume. |
| Regulatory Issues | Different regions have varying regulations for blockchain use. |
| Energy Consumption | Blockchain mining can be energy-intensive and costly. |
| Interoperability | Different blockchains may not easily integrate. |
Addressing these challenges is key to unlocking blockchain’s full potential in cyber security. By overcoming these hurdles, blockchain can offer a secure and efficient solution for the future.

Credit: www.weforum.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Will Blockchain Replace Cyber Security?
Blockchain will not replace cyber security. It enhances security but cannot cover all aspects. Both are needed for comprehensive protection.
What Is The Use Case Of Blockchain In Security?
Blockchain enhances security by providing a decentralized ledger, ensuring data integrity, preventing fraud, and enabling secure transactions.
What Is The Blockchain Revolution In Cyber Security?
The blockchain revolution enhances cybersecurity by providing decentralized, tamper-proof data storage. This reduces hacking risks and ensures data integrity. Blockchain’s transparency also helps in better tracking and auditing of transactions. These features make it a robust solution for securing sensitive information.
What Is Blockchain In Cyber Law?
Blockchain in cyber law refers to the legal framework governing blockchain technology. It covers data security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. This ensures blockchain’s lawful application and protects user rights.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers securely.
How Does Blockchain Enhance Cybersecurity?
Blockchain enhances cybersecurity by providing transparent, immutable records, reducing fraud, and decentralizing data storage.
Can Blockchain Prevent Cyber Attacks?
Blockchain can reduce cyber attacks by eliminating single points of failure and ensuring data integrity.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers robust solutions for enhancing cyber security. Its decentralized nature makes data breaches difficult. Implementing blockchain can greatly improve security protocols. This innovation is essential for safeguarding sensitive information. Embrace blockchain to stay ahead in the cyber security landscape.
Secure your digital assets with this cutting-edge technology.


